Urogenital hiatus
| Urogenital hiatus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | hiatus urogenitalis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
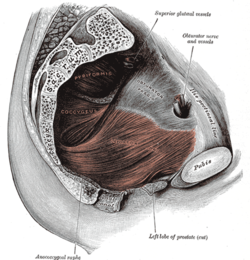
The urogenital hiatus is a large midline opening[1] in the anteromedial part of the pelvic floor (more precisely, the pubococcygeal muscle),[2] extending between the pubis (anteriorly), and rectum (posteriorly). Each levator ani muscle forms either lateral border of the hiatus.[1]
The hiatus acccomodates the apex of the prostate in males,[1] and gives passage to the urethra in both sexes, the vagina in females, the deep dorsal vein of clitoris (females) or penis (males),[2] and nerves of the penis in males.[1]
Clinical significance[edit]
The urogenital hiatus has been linked to urinary stress incontinence.[3]
See also[edit]
- Coccyx (tailbone)
- Pubococcygeus muscle
- Pelvic floor dysfunction
- Perineology
- Perineal hernia
- Female genital prolapse
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d "urogenital hiatus - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2024-05-21.
- ^ a b "urogenital hiatus". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2023-06-14.
- ^ Huang, W. C.; Yang, S. H.; Yang, J. M. (2006). "Anatomical and functional significance of urogenital hiatus in primary urodynamic stress incontinence". Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 27 (1): 71–7. doi:10.1002/uog.2649. PMID 16323154. S2CID 22170424.
