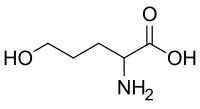
Hydroxyaminovaleric acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
5-Hydroxynorvaline
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H11NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 133.147 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 218–220 °C (424–428 °F; 491–493 K) 224 °C for L-enantiomer |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hydroxyaminovaleric acid (HAVA) is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. A white solid, it is a rarely encountered amino acid.[1] It is also produced by reduction of glutamate-5-semialdehyde residues followed by proteolysis.[2]
References[edit]
- ^ Chenault, H. Keith; Dahmer, Juergen; Whitesides, George M. (1989). "Kinetic resolution of unnatural and rarely occurring amino acids: Enantioselective hydrolysis of N-acyl amino acids catalyzed by acylase I". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 111 (16): 6354–6364. doi:10.1021/ja00198a055.
- ^ Requena, J. R.; Levine, R. L.; Stadtman, E. R. (2003). "Recent Advances in the Analysis of Oxidized Proteins". Amino Acids. 25 (3–4): 221–226. doi:10.1007/s00726-003-0012-1. PMID 14661085. S2CID 28837698.
